Kedoshim

Kedoshim (“Holy”) opens by instructing the Israelites to be holy. It details dozens of laws regulating all aspects of life, including observing Shabbat, loving one’s neighbor, and leaving portions of a field for the poor. It ends by detailing punishments for certain types of idolatry and sexual misconduct.
Aharei Mot

Aharei Mot (“After The Death”) opens by describing the ritual service of Yom Kippur, the Day of Atonement. It then details the prohibitions of offering sacrifices outside of the Mishkan (Tabernacle) and of eating animal blood, and ends with a list of forbidden sexual relations.
Metzora

Metzora opens by describing the purification process and accompanying sacrifices for one infected with tzaraat, a discoloration condition on the skin. It then describes the process of treating a house infected with tzaraat and the ritual impurity generated by certain bodily discharges.
Tazria

Tazria (“She Bears Seed”) opens by describing the purification process for a woman after childbirth. It then describes different forms of tzaraat, a discoloration condition on skin or clothing, and the requirement of an infected person to dwell alone outside the camp and be inspected by a priest.
Shemini

Shemini (“Eighth”) opens with the consecration of the Mishkan (Tabernacle). Two of Aaron’s sons are consumed by a fire sent from God when they attempt to offer a “strange fire.” God describes the animals, birds, and fish that are permissible and prohibited for consumption, as well as some laws of ritual purity.
Tzav
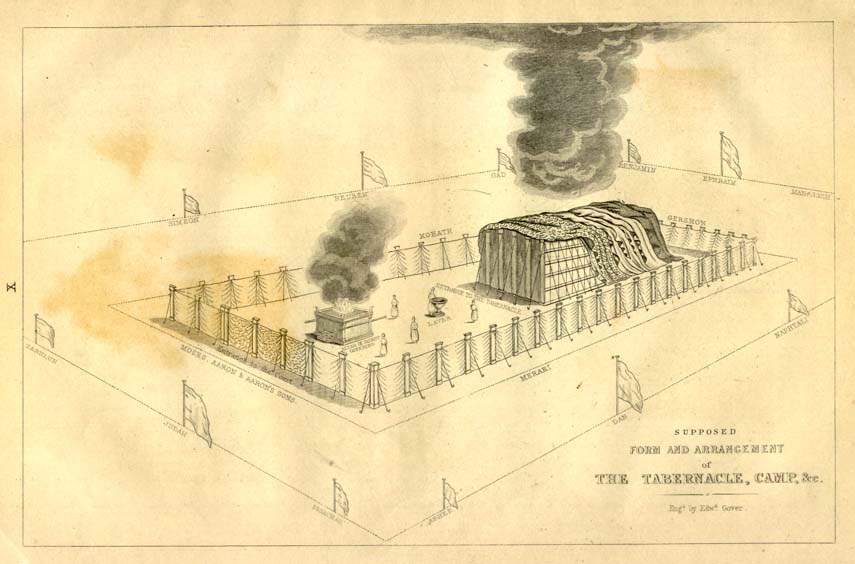
In Tzav (“Command”), God tells Moses about the sacrifices offered in the Mishkan (Tabernacle), including a meal offering brought by the high priest, guilt offerings, and offerings of thanks. Moses initiates Aaron and Aaron’s sons for priestly service in the Mishkan.
Vayikra
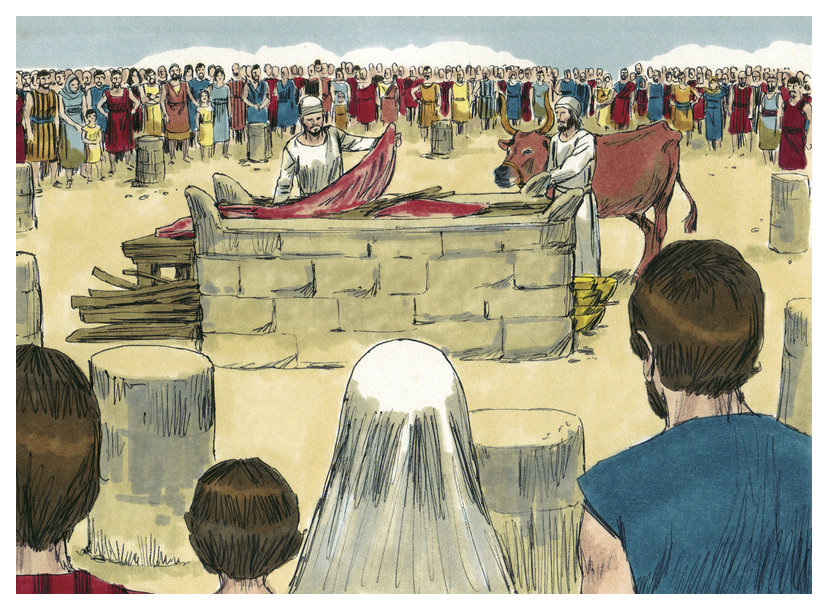
In Vayikra (“He Called”), the first Torah portion in the Book of Leviticus, God tells Moses about the sacrifices offered in the Mishkan (Tabernacle). Among these are sacrifices entirely burnt on the altar, meal offerings made of flour and oil, peace offerings, and sacrifices brought for sinning inadvertently.
Pekudei
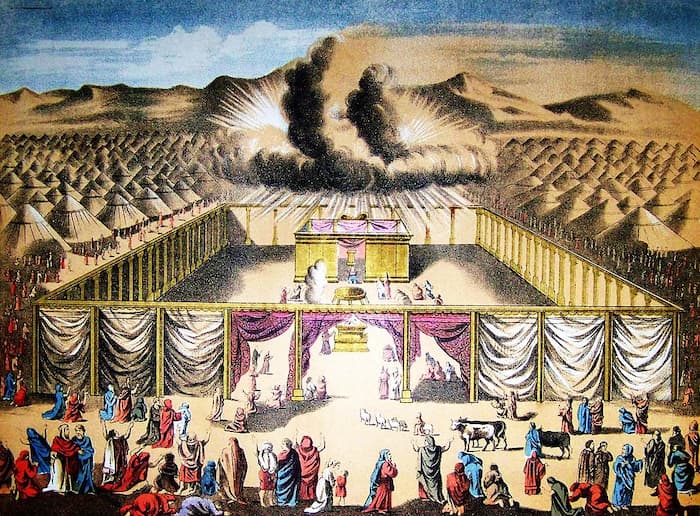
Pekudei (“Accountings Of”) is the final Torah reading in the Book of Exodus. It describes the making of priestly garments worn in the Mishkan (Tabernacle) and the completion of its construction. At God’s command, Moses erects the Mishkan and puts its vessels in place, and God’s presence fills the Mishkan.
Vayakhel
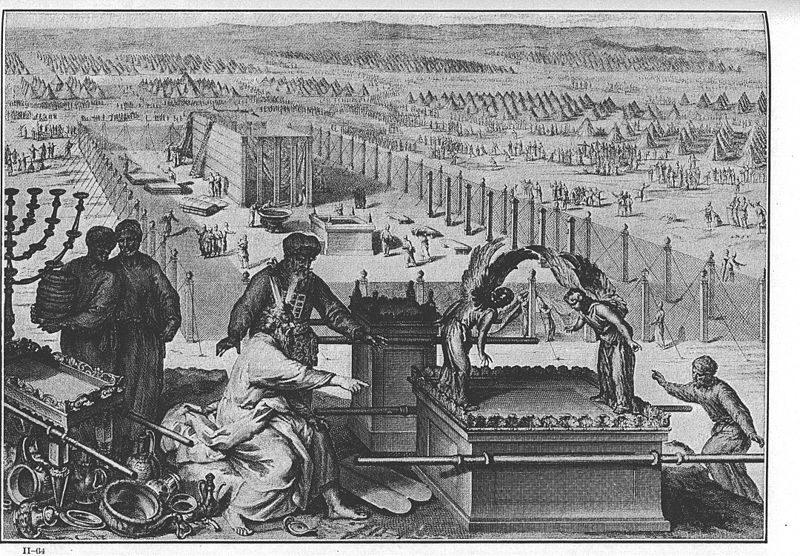
Vayakhel (“He Assembled”) opens as God commands the Israelites to observe the Sabbath. Moses asks for material donations for the building of the Mishkan (Tabernacle), and the people donate. A group of artisans designated by God begin building the Mishkan and its vessels.
Ki Tisa
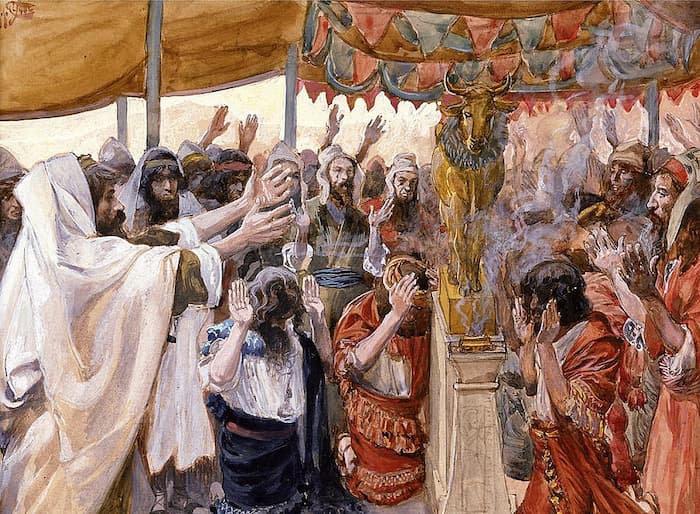

Ki-Tisa (“When You Elevate”) opens as God tells Moses to collect a half-shekel donation from all Israelites and to anoint the Mishkan (Tabernacle), its vessels, and the priests. The Israelites worship the golden calf and Moses breaks the tablets. Moses beseeches God to forgive, and returns with a second set of tablets.
